For every business user, data security is the first concern while purchasing a new software for business. MS Dynamics CRM is a software application that is designed keeping such concerns in mind. As a move in the direction of improved data security, Dynamics has introduced a new security model.
The main features of the security model are:
- Users can access only that data, which is appropriate for their job, not any other.
- Different roles are introduced and data access is given based on these roles.
- Users will be able to share data with others without giving ownership.
Types of Security in Dynamics CRM
MS Dynamics CRM provides three types of security:
- Role-based security
- Record based security
- Field level security
Role-based security: It provides a specific set of privileges to a user in Dynamics CRM.
For example: If we want all users with the security role of sales manager to have read, write, and delete access to all Lead records while users with the security role of salesperson should have only read access to the Leads they own, role-based security settings help accomplish this.
Record-based security: It allows or restricts access to specific records in the CRM.
For example: If we want to restrict a set of users from accessing Case records, record-based security helps accomplish this.
Field level security: It allows or restricts access to specific fields on an entity in Dynamics CRM.
For example: If we want only a set of users to see a specific field (Annual Revenue, for instance) on the Lead entity, field-based security can hide or display that field, based on users.

Security Roles in MS Dynamics
In Dynamics, different security roles are introduced based on which data access levels are set. They define the privileges and access levels for various entities in CRM. Each security role is categorized into eight sections. They are Core records, Sales, Service, Marketing, Business Management, Service Management, Customization, and Custom Entities.
The list of default security roles available in CRM are:
- System Administrator
- System Customizer
- CEO
- Sales Manager
- Sales Person
- Other Standard Roles.
Creating a Security Role in Dynamics
A new security role can be created in different ways.
- To create a security role from scratch
- To modify a CRM default role
- To copy an existing role and modify its privileges.
The ideal way to create a new security role is to copy an existing role and then modify its privileges. Dynamics CRM contains 580 predefined privileges, so it is difficult to create a new security role from scratch.
For doing this:
1. Navigate to Settings-> Security->Security Roles
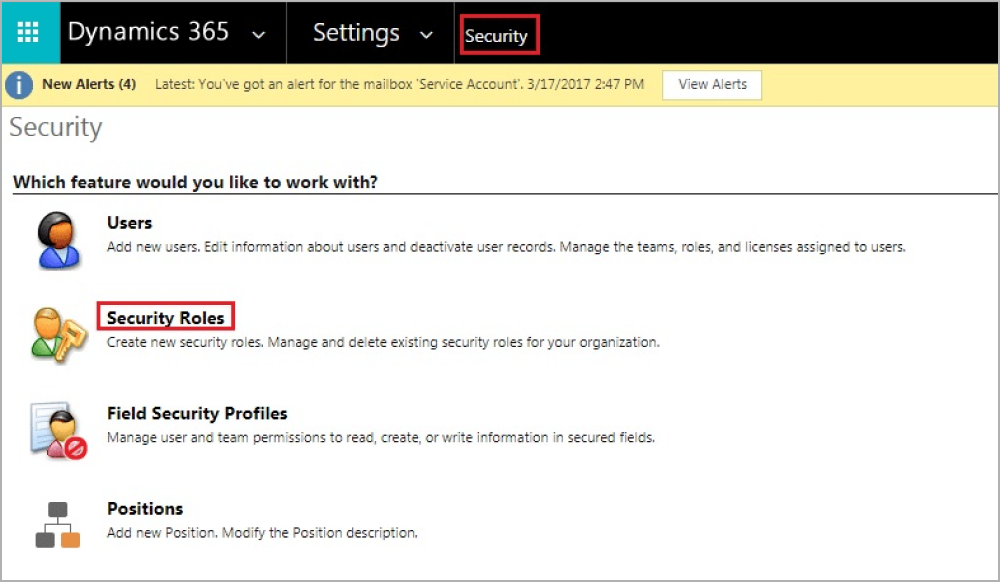
2. Select the Security Role that you want to copy.
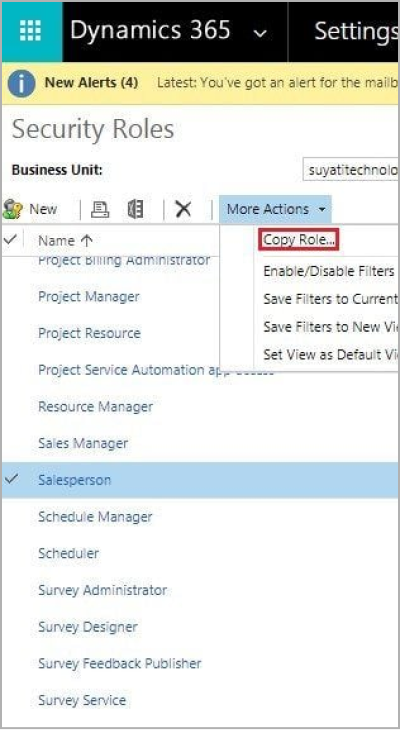
3. On Actions toolbar, select more options and then choose Copy Role.
4. A new dialogue box appears. Name the new Security Role here.
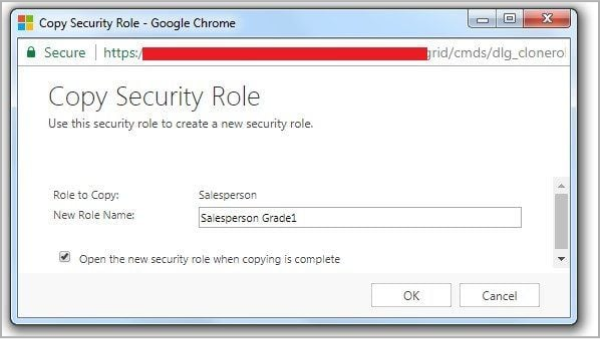
5. Click OK, and once copying is complete, open the Security Role and modify it based on your needs.
Related: Understanding the purpose of Business rules in MS Dynamics CRM
Privileges determine the level of access a user has to a specific record or its type. The following are the set of privileges associated with each Security Role in CRM.
Create: Allows the user to create a new record in CRM.
Read: Allows a user to view a record in CRM.
Write: Allows a user to edit a record in CRM.
Delete: Allows a user to delete a record in CRM.
Append: Allows the user to attach other entities to a record (e.g. Notes).
Append to: Allows the user to attach other entities with a record (e.g. Account).
Assign: Allows assigning ownership of a record to another user.
Share: Allows to share the record information with another user by keeping the ownership.
Related: A step-by-step guide to configuring emails in MS Dynamics CRM
To View or Set Privileges to a Security Role
1. Navigate to Settings-> Security->Security Roles
It will list all the security roles available in CRM. Open the security role that you want to modify. You can set privileges to that security role based on the various access levels provided.
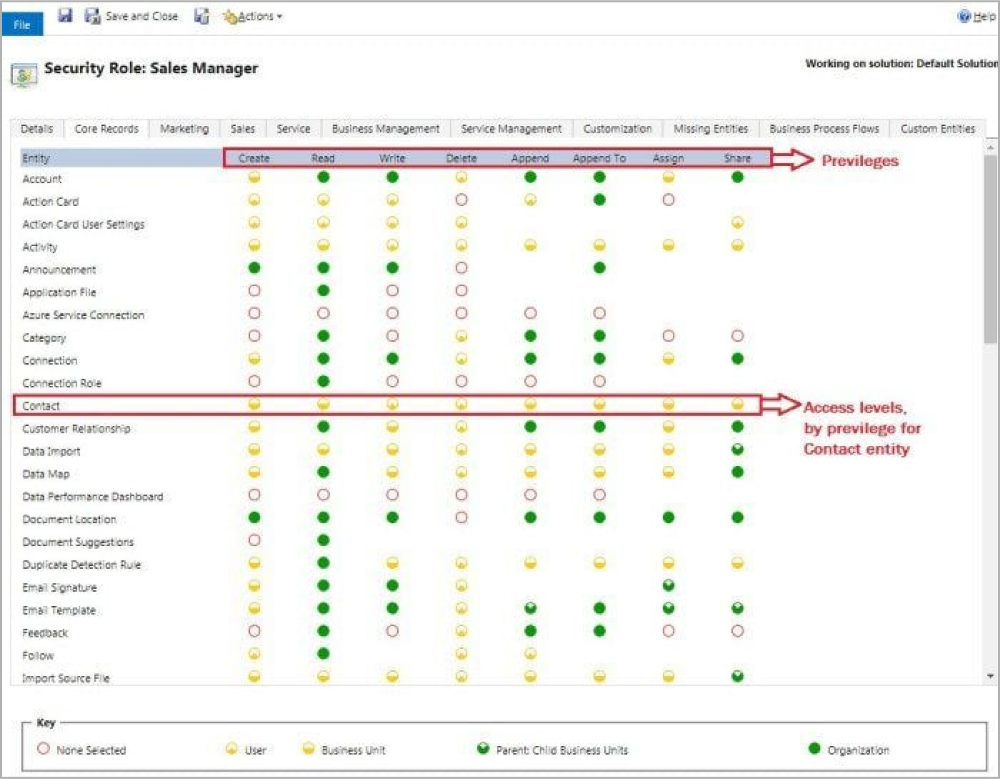
Levels of Access
None: No Privileges given.
User (Basic): The privilege will be given to the records owned by the user and the team to which the user belongs.
Business Unit (Local): Privileges to records owned by the business unit to which the user belongs.
Parent (Deep): Privileges to the records owned by the parent business unit to which the user belongs and the child business units associated with that business unit.
Organization (Global): Privileges for all records in the organization regardless of who owns it.
The MS Dynamics security model protects data integrity and privacy, which opens up new and safer opportunities for data access and collaboration. If you want to know more about the security model, write to itsolutions@milestone.tech. You could also leave us your questions/thoughts in the comments section below, and we will get back to you soon.




